AC charging and DC charging are the two most popular charging standards for electric vehicles today. Each type offers different charging speeds, costs and usage. Understanding and distinguishing between AC charging and DC charging will help users make the most suitable choice for their travel needs and actual installation conditions.
What is an AC charger? How does it work?
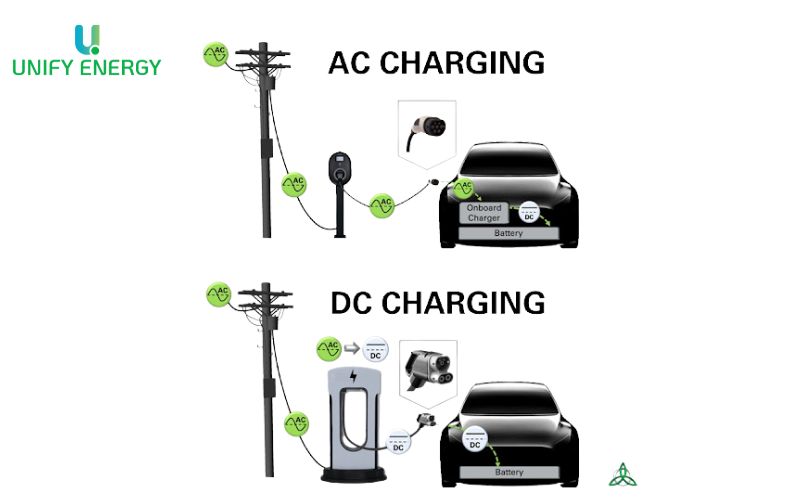
AC Charger: Alternating current (AC) is the most common form of electricity on the grid, used to power everything from lights to industrial machinery. However, electric vehicle (EV) batteries can only store direct current (DC) electricity, so AC needs to be converted to DC before charging the battery.
How it works: When a car is plugged into an AC charging station—typically found at home or at slow-speed public charging stations—the car’s built-in charger handles the conversion. While the conversion is stable and safe, it takes longer, making AC charging slower than DC charging. Still, the low cost and low stress on the battery make AC charging ideal for frequent, everyday charging.
>>> See more: AC charger for electric vehicles suitable for all new car models

What is a DC charger? How does it work?
DC Charger: Direct current (DC) is a type of electricity that is directly compatible with the way electric vehicle (EV) batteries store energy. Therefore, DC charging allows for charging without the need for conversion in the vehicle. Unlike AC charging, DC chargers perform the entire conversion process from AC to DC right at the charging station, before transferring electricity to the battery, significantly reducing charging time.
How it works: When the car is connected to a DC charging station — usually a fast charging station at a highway stop or service station — the pre-converted electricity goes directly to the battery through a special charging port. Thanks to its high power (usually between 50kW and 350kW), DC chargers can charge the battery to 80% capacity in just 20–40 minutes. Although expensive to invest in and not suitable for everyday charging, DC charging is the ideal solution for long journeys or when you need to recharge quickly.
>>> See more: DC charger for electric vehicles helps save charging time

How are AC and DC electric vehicle charging stations different?
The difference between AC charging and DC charging is mainly in the power conversion mechanism, charging speed and flexibility in actual usage scenarios.
Conversion process
With an AC (alternating current) charging station, electricity from the grid is supplied in the form of AC, then converted to DC by the charger built into the vehicle. This conversion depends on the processing capacity of each vehicle model, and is the reason why charging speed is limited.
In contrast, a DC (direct current) charging station performs the conversion right at the charger outside the station, then injects DC power directly into the battery. Thanks to that, the charging process is much faster, not limited by the capacity of the charger on the vehicle.
Impact on charging time
The difference in the power conversion mechanism makes DC charging stations have superior charging speed compared to AC charging. AC charging stations usually take 4-8 hours to fully charge the battery, suitable for overnight charging at home or at work. Meanwhile, DC charging stations can charge 80% of the battery in just 20-40 minutes, suitable for long trips or when urgent charging is needed.
Flexible in many usage situations
AC charging stations are low-cost, easy to install, battery-friendly, and suitable for everyday use. Users can charge their vehicles at home, office parking lots, or shopping malls without the need for overly complex infrastructure.
In contrast, DC charging stations are often installed at highway stops, service stations, or large-scale public stations (where users need to recharge quickly). However, due to their large capacity and high cost, DC charging is less common and is often used in special or emergency situations.
Types of electric vehicle charging stations currently operating in Vietnam
3 types of electric vehicle charging stations commonly operated in Vietnam include:
Normal charging 11 kW
This is a low-power alternating current (AC) charging station, usually installed at home, apartment parking lots or long-term parking areas. The average charging time is about 6-8 hours to fully charge the battery, suitable for overnight charging. The advantages are low cost, easy deployment and do not put much pressure on the car battery.
30kW fast charging
It is a medium-power DC charger that can charge 0-80% of the battery in about 1-2 hours depending on the battery capacity of the vehicle. Suitable for public parking lots, offices or shopping malls.
60kW fast charging
These stations have a higher capacity, which significantly reduces charging times – it only takes about 30–60 minutes to charge most of the battery. They are often deployed at long-distance rest stops, service stations, or areas with high traffic volumes.

Unify Energy – A reputable and genuine supplier of AC and DC chargers
Unify Energy is a reputable unit specializing in providing genuine AC and DC chargers, ensuring quality, safety and suitability for many types of electric vehicles. We provide desktop AC chargers, wall-mounted chargers or DC chargers with capacity up to 120KW.
We are committed to international quality products, a dedicated technical staff to support customers 24/7 and a long-term warranty policy, affirming the quality of products provided by Unify Energy. For any questions, please contact Hotline: 096 898 7880 for support.
Conclude
Distinguishing between AC and DC charging not only helps electric vehicle users understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type, but is also the key to choosing the optimal charging solution. Based on usage habits and available infrastructure, you can determine the most suitable charging type, flexibly combining both AC and DC. This approach ensures that the vehicle is always ready, while providing convenience, saving time and maximizing operating efficiency.
>>> You may be interested in: Instructions for using DC fast charging properly to increase battery life








Leave a Reply